Tratos XLPE/SWA/LS0H – RTE4OM1FM1
Energy Cables / Low Voltage Cables - LV / LV Energy Cables IEC Special Cables / Oil & Gas Cables / Petrochemical Cables
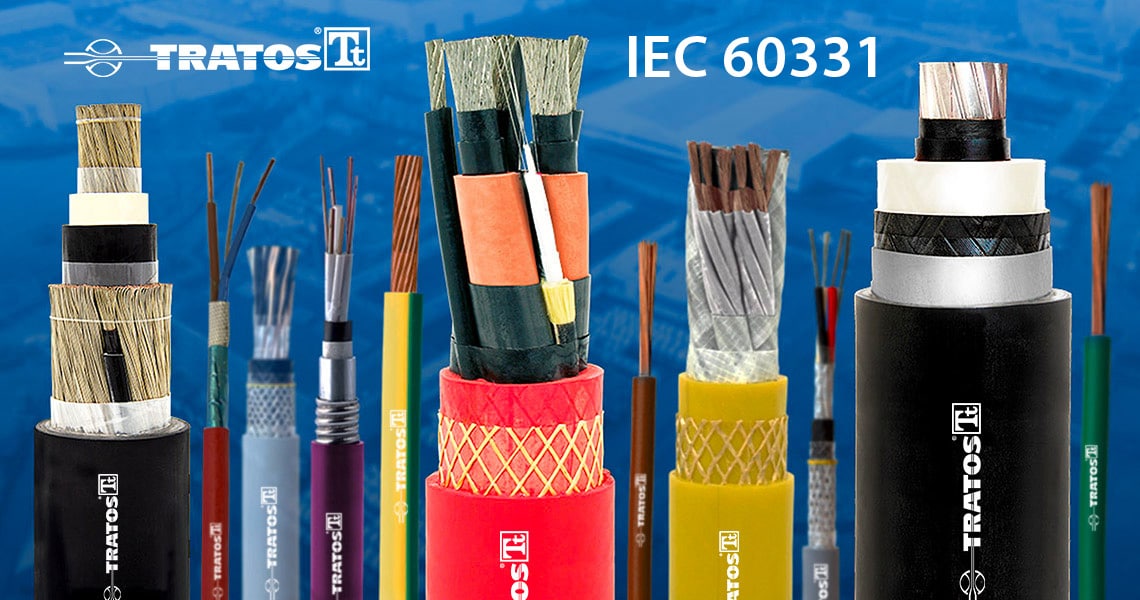

IEC 60331 is an essential international standard that defines test methods to assess the circuit integrity of electric cables when exposed to fire conditions. These tests ensure that cables can continue to operate for a specified duration under extreme heat and mechanical stress, maintaining functionality crucial for safety systems in buildings, transportation, and industrial applications.
IEC 60331 cable standard comprises a number of sections, perhaps the four most important being:
IEC 60331-1 standard specifies the test method for assessing the circuit integrity of cables when exposed to fire and mechanical shock under controlled conditions. The test is designed to simulate real-world fire scenarios where cables may be subjected to mechanical impacts while under extreme heat. It applies to cables with a rated voltage up to and including 0.6/1.0 kV, including metallic data, telecom cables, and optical fibre cables. The standard is specifically intended for cables with an overall diameter exceeding 20 mm, ensuring that larger cables used in critical infrastructure meet stringent fire safety requirements. Smaller diameter cables fall under the testing criteria of IEC 60331-2.
This test method is essential for industries such as energy, telecommunications, transportation, and emergency services. Maintaining circuit integrity in fire conditions is crucial for operational safety and compliance with regulatory requirements.
IEC 60331-2 standard specifies the test method for assessing the circuit integrity of cables when exposed to fire and mechanical shock under controlled conditions. This test applies to cables with a rated voltage up to and including 0.6/1.0 kV, including metallic data, telecom cables, and optical fibre cables. It is specifically designed for cables with an overall diameter not exceeding 20 mm, ensuring that smaller cables used in critical applications meet strict fire safety requirements. Cables with a larger diameter fall under the testing criteria of IEC 60331-1.
This test method is crucial for industries such as energy, telecommunications, transportation, and emergency services. Ensuring that cables maintain circuit integrity during fire incidents is vital for operational safety and regulatory compliance.
IEC 60331-3 standard specifies a test method for evaluating the circuit integrity of cables when subjected to fire and mechanical shock while enclosed in a metal enclosure. This distinguishes it from IEC 60331-1 and IEC 60331-2, which assess cables in open environments. The test applies to cables with a rated voltage up to and including 0.6/1.0 kV, including metallic data, telecom cables, and optical fibre cables, and is intended for cables with an overall diameter not exceeding 20 mm. Cables of larger diameter fall under IEC 60331-1.
This testing method is essential for applications where cables are installed within metal conduits, ducts, or other protective enclosures. Industries such as transportation, energy, telecommunications, and emergency infrastructure rely on this standard to ensure cable functionality in extreme conditions.
IEC 60331-4 standard specifies the test method for evaluating the circuit integrity of power cables with a rated voltage higher than 0.6/1.0 kV up to and including 18/30 kV when subjected to fire and mechanical shock under controlled conditions. Unlike IEC 60331-1, IEC 60331-2, and IEC 60331-3, which focus on lower-voltage cables, this standard is specifically designed for high-voltage cables used in critical applications where maintaining power supply during fire incidents is essential.
The test is restricted to conductor sizes up to and including 120 mm². However, test results for 120 mm² conductors qualify larger cross-sections of the same cable construction. For preassembled three-core cables, a complete single-core test qualifies the entire cable.
IEC 60331-4 standard is essential for industries such as energy distribution, industrial power systems, and critical infrastructure, where fire-resistant high-voltage cables play a crucial role in operational safety and regulatory compliance.
Energy Cables / Low Voltage Cables - LV / LV Energy Cables IEC Special Cables / Oil & Gas Cables / Petrochemical Cables
Energy Cables / Low Voltage Cables - LV / LV Energy Cables IEC
Special Cables / Oil & Gas Cables / Oil & Gas JBA Special Cables / Fire Resistant Cables / Tratos Firesafe JBA® IEC
Special Cables / Oil & Gas Cables / Oil & Gas JBA Special Cables / Fire Resistant Cables / Tratos Firesafe JBA® IEC
Special Cables / Fire Resistant Cables / Tratos Firesafe JBA® IEC
Special Cables / Fire Resistant Cables / Tratos Firesafe® BS
Special Cables / Oil & Gas Cables / Oil & Gas JBA Special Cables / Fire Resistant Cables / Tratos Firesafe JBA® IEC
Special Cables / Fire Resistant Cables / Tratos Firesafe JBA® IEC
Please, don’t hesitate to contact us for additional information on our company or our products.
Our website uses cookies and thereby collects information about your visit to improve our website (by analyzing), show you Social Media content and relevant advertisements. Please see our cookies page for further details or agree by clicking the 'Accept' button.
Below you can choose which kind of cookies you allow on this website. Click on the "Save cookie settings" button to apply your choice.
This content is blocked. Accept cookies within the '%CC%' category to view this content.